Tasty
Tasty is a modern testing framework for Haskell.
It lets you combine your unit tests, golden tests, QuickCheck/SmallCheck
properties, and any other types of tests into a single test suite.
Features:
- Run tests in parallel but report results in a deterministic order
- Filter the tests to be run using patterns specified on the command line
- Hierarchical, colored display of test results
- Reporting of test statistics
- Acquire and release resources (sockets, temporary files etc.) that can be
shared among several tests
- Extensibility: add your own test providers and ingredients (runners) above and
beyond those provided

To find out what's new, read the change log.
Ask any tasty-related questions on the mailing list or IRC channel
#tasty at FreeNode (logs & stats).
Example
Here's how your test.hs might look like:
import Test.Tasty
import Test.Tasty.SmallCheck as SC
import Test.Tasty.QuickCheck as QC
import Test.Tasty.HUnit
import Data.List
import Data.Ord
main = defaultMain tests
tests :: TestTree
tests = testGroup "Tests" [properties, unitTests]
properties :: TestTree
properties = testGroup "Properties" [scProps, qcProps]
scProps = testGroup "(checked by SmallCheck)"
[ SC.testProperty "sort == sort . reverse" $
\list -> sort (list :: [Int]) == sort (reverse list)
, SC.testProperty "Fermat's little theorem" $
\x -> ((x :: Integer)^7 - x) `mod` 7 == 0
-- the following property does not hold
, SC.testProperty "Fermat's last theorem" $
\x y z n ->
(n :: Integer) >= 3 SC.==> x^n + y^n /= (z^n :: Integer)
]
qcProps = testGroup "(checked by QuickCheck)"
[ QC.testProperty "sort == sort . reverse" $
\list -> sort (list :: [Int]) == sort (reverse list)
, QC.testProperty "Fermat's little theorem" $
\x -> ((x :: Integer)^7 - x) `mod` 7 == 0
-- the following property does not hold
, QC.testProperty "Fermat's last theorem" $
\x y z n ->
(n :: Integer) >= 3 QC.==> x^n + y^n /= (z^n :: Integer)
]
unitTests = testGroup "Unit tests"
[ testCase "List comparison (different length)" $
[1, 2, 3] `compare` [1,2] @?= GT
-- the following test does not hold
, testCase "List comparison (same length)" $
[1, 2, 3] `compare` [1,2,2] @?= LT
]
And here is the output of the above program:
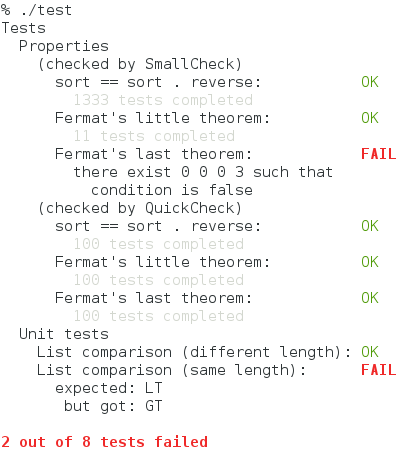
(Note that whether QuickCheck finds a counterexample to the third property is
determined by chance.)
Packages
tasty is the core package. It contains basic definitions and APIs and a
console runner.
In order to create a test suite, you also need to install one or more «providers» (see
below).
Providers
The following providers exist:
It's easy to create custom providers using the API from Test.Tasty.Providers.
Ingredients
Ingredients represent different actions that you can perform on your test suite.
One obvious ingredient that you want to include is one that runs tests and
reports the progress and results.
Another standard ingredient is one that simply prints the names of all tests.
It is possible to write custom ingredients using the API from Test.Tasty.Runners.
Some ingredients that can enhance your test suite are:
- tasty-ant-xml adds a
possibility to write the test results in a machine-readable XML format, which
is understood by various CI systems and IDEs
- tasty-rerun adds support for
minimal test reruns by recording previous test runs and using this information
to filter the test tree. For example, you can use this ingredient to only run
failed tests, or only run tests that threw an exception.
- tasty-html adds the
possibility to write the test results as a HTML file
- tasty-stats adds the
possibility to collect statistics of the test suite in a CSV file.
Other packages
- tasty-th automatically
discovers tests based on the function names and generate the boilerplate code for
you
- tasty-hunit-adapter
converts existing HUnit test suites into tasty test suites
- tasty-discover automatically discovers
your tests.
- tasty-expected-failure provides
test markers for when you expect failures or wish to ignore tests.
Options
Options allow one to customize the run-time behavior of the test suite, such
as:
- mode of operation (run tests, list tests, run tests quietly etc.)
- which tests are run (see «Patterns» below)
- parameters of individual providers (like depth of search for SmallCheck)
Setting options
There are two main ways to set options:
Runtime
When using the standard console runner, the options can be passed on the
command line or via environment variables. To see the available options, run
your test suite with the --help flag. The output will look something like this
(depending on which ingredients and providers the test suite uses):
% ./test --help
Mmm... tasty test suite
Usage: test [-p|--pattern ARG] [-t|--timeout ARG] [-l|--list-tests]
[-j|--num-threads ARG] [-q|--quiet] [--hide-successes] [--color ARG]
[--quickcheck-tests ARG] [--quickcheck-replay ARG]
[--quickcheck-show-replay ARG] [--quickcheck-max-size ARG]
[--quickcheck-max-ratio ARG] [--quickcheck-verbose]
[--smallcheck-depth ARG]
Available options:
-h,--help Show this help text
-p,--pattern ARG Select only tests that match pattern
-t,--timeout ARG Timeout for individual tests (suffixes: ms,s,m,h;
default: s)
-l,--list-tests Do not run the tests; just print their names
-j,--num-threads ARG Number of threads to use for tests execution
-q,--quiet Do not produce any output; indicate success only by
the exit code
--hide-successes Do not print tests that passed successfully
--color ARG When to use colored output. Options are 'never',
'always' and 'auto' (default: 'auto')
--quickcheck-tests ARG Number of test cases for QuickCheck to generate
--quickcheck-replay ARG Replay token to use for replaying a previous test run
--quickcheck-show-replay ARG
Show a replay token for replaying tests
--quickcheck-max-size ARG
Size of the biggest test cases quickcheck generates
--quickcheck-max-ratio ARG
Maximum number of discared tests per successful test
before giving up
--quickcheck-verbose Show the generated test cases
--smallcheck-depth ARG Depth to use for smallcheck tests
Every option can be passed via environment. To obtain the environment variable
name from the option name, replace hyphens - with underscores _, capitalize
all letters, and prepend TASTY_. For example, the environment equivalent of
--smallcheck-depth is TASTY_SMALLCHECK_DEPTH. To turn on a switch (such as
TASTY_HIDE_SUCCESSES), set the variable to True.
If you're using a non-console runner, please refer to its documentation to find
out how to configure options during the run time.
Compile-time
You can also specify options in the test suite itself, using
localOption. It can be applied not only to the whole test tree, but also to
individual tests or subgroups, so that different tests can be run with
different options.
It is possible to combine run-time and compile-time options, too, by using
adjustOption. For example, make the overall testing depth configurable
during the run time, but increase or decrease it slightly for individual
tests.
This method currently doesn't work for ingredient options, such as --quiet or
--num-threads. You can set them by setting the corresponding environment
variable before calling defaultMain:
import Test.Tasty
import System.Environment
main = do
setEnv "TASTY_NUM_THREADS" "1"
defaultMain _
Patterns
It is possible to restrict the set of executed tests using the --pattern
option. The syntax of patterns is the same as for test-framework, namely:
- An optional prefixed bang
! negates the pattern.
- If the pattern ends with a slash, it is removed for the purpose of
the following description, but it would only find a match with a
test group. In other words,
foo/ will match a group called foo
and any tests underneath it, but will not match a regular test
foo.
- If the pattern does not contain a slash
/, the framework checks
for a match against any single component of the path.
- Otherwise, the pattern is treated as a glob, where:
- The wildcard
* matches anything within a single path component
(i.e. foo but not foo/bar).
- Two wildcards
** matches anything (i.e. foo and foo/bar).
- Anything else matches exactly that text in the path (i.e.
foo
would only match a component of the test path called foo (or a
substring of that form).
For example, group/*1 matches group/test1 but not
group/subgroup/test1, whereas both examples would be matched by
group/**1. A leading slash matches the beginning of the test path; for
example, /test* matches test1 but not group/test1.
Running tests in parallel
In order to run tests in parallel, you have to do the following:
- Compile (or, more precisely, link) your test program with the
-threaded
flag;
- Launch the program with
+RTS -N -RTS.
Timeout
To apply timeout to individual tests, use the --timeout (or -t) command-line
option, or set the option in your test suite using the mkTimeout function.
Timeouts can be fractional, and can be optionally followed by a suffix ms
(milliseconds), s (seconds), m (minutes), or h (hours). When there's no
suffix, seconds are assumed.
Example:
./test --timeout=0.5m
sets a 30 seconds timeout for each individual test.
Options controlling console output
The following options control behavior of the standard console interface:
-q,--quiet-
Run the tests but don't output anything. The result is indicated only by the
exit code, which is 1 if at least one test has failed, and 0 if all tests
have passed. Execution stops when the first failure is detected, so not all
tests are necessarily run.
This may be useful for various batch systems, such as commit hooks.
--hide-successes- Report only the tests that has failed. Especially useful when the
number of tests is large.
-l,--list-tests- Don't run the tests; only list their names, in the format accepted by
--pattern.
--color- Whether to produce colorful output. Accepted values:
never,
always, auto. auto means that colors will
only be enabled when output goes to a terminal and is the default value.
Custom options
It is possible to add custom options, too.
To do that,
- Define a datatype to represent the option, and make it an instance of
IsOption
- Register the options with the
includingOptions ingredient
- To query the option value, use
askOption.
See the Custom options in Tasty article for some examples.
Project organization and integration with Cabal
There may be several ways to organize your project. What follows is not
Tasty's requirements but my recommendations.
Tests for a library
Place your test suite sources in a dedicated subdirectory (called tests
here) instead of putting them among the main library sources.
The directory structure will be as follows:
my-project/
my-project.cabal
src/
...
tests/
test.hs
Mod1.hs
Mod2.hs
...
test.hs is where your main function is defined. The tests may be
contained in test.hs or spread across multiple modules (Mod1.hs, Mod2.hs,
...) which are then imported by test.hs.
Add the following section to the cabal file (my-project.cabal):
test-suite test
default-language:
Haskell2010
type:
exitcode-stdio-1.0
hs-source-dirs:
tests
main-is:
test.hs
build-depends:
base >= 4 && < 5
, tasty >= 0.7 -- insert the current version here
, my-project -- depend on the library we're testing
, ...
Tests for a program
All the above applies, except you can't depend on the library if there's no
library. You have two options:
- Re-organize the project into a library and a program, so that both the
program and the test suite depend on this new library. The library can be
declared in the same cabal file.
- Add your program sources directory to the
Hs-source-dirs. Note that this
will lead to double compilation (once for the program and once for the test
suite).
FAQ
-
How do I make some tests execute after others?
Currently, your only option is to make all tests execute sequentially by
setting the number of tasty threads to 1 (example).
See #48 for the discussion.
Press
Blog posts and other publications related to tasty. If you wrote or just found
something not mentioned here, send a pull request!
Background
Tasty is heavily influenced by test-framework.
The problems with test-framework are:
- Poor code style (some lines of the code wouldn't even fit in a twitter message!)
- Poor architecture — e.g. relying on laziness for IO and control flow. The
whole story with
:~> and ImprovingIO is really obscure.
- Non-extensible options. For example, when I integrated SmallCheck with
test-framework (in the form of the
test-framework-smallcheck package), I
still had to submit patches to the main package to make SmallCheck depth
customizable by the user.
- The project is effectively unmaintained.
So I decided to recreate everything that I liked in test-framework from scratch
in this package.
Maintainers
Roman Cheplyaka is the primary maintainer.
Oliver Charles is the backup maintainer. Please
get in touch with him if the primary maintainer cannot be reached.



