# co-log
[](https://hackage.haskell.org/package/co-log)
[](https://github.com/kowainik/co-log/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](https://travis-ci.org/kowainik/co-log)
Logging library based on [`co-log-core`](../co-log-core) package. Provides
ready-to-go implementation of logging. This README contains _How to_ tutorial on
using this library. This tutorial explains step by step how to integrate
`co-log` into small basic project, specifically how to replace `putStrLn` used
for logging with library provided logging.
All code below can be compiled and run with the following commands:
```shell
$ cabal new-build co-log
$ cabal new-exec readme
```
## Preamble: imports and language extensions
Since this is a literate haskell file, we need to specify all our language
extensions and imports up front.
```haskell
{-# LANGUAGE FlexibleContexts #-}
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}
import Colog (Message, WithLog, cmap, fmtMessage, logDebug, logInfo, logTextStdout, logWarning,
usingLoggerT)
import Control.Monad.IO.Class (MonadIO, liftIO)
import qualified Data.Text as Text
import qualified Data.Text.IO as TextIO
```
## Simple IO function example
Consider the following function that reads lines from `stdin` and outputs
different feedback depending on the line size.
```haskell
processLinesBasic :: IO ()
processLinesBasic = do
line <- TextIO.getLine
case Text.length line of
0 -> do
-- here goes logging
TextIO.putStrLn ">>>> Empty input"
processLinesBasic
n -> do
TextIO.putStrLn ">>>> Correct input"
TextIO.putStrLn $ "Line length: " <> Text.pack (show n)
```
This code mixes application logic with logging of the steps. It's convenient to
have logging to observe behavior of the application. But `putStrLn` is very
simple and primitive way to log things.
## Using `co-log` library
In order to use `co-log` library, we need to refactor `processLinesBasic`
function in the following way:
```haskell
processLinesLog :: (WithLog env Message m, MonadIO m) => m ()
processLinesLog = do
line <- liftIO TextIO.getLine
case Text.length line of
0 -> do
-- here goes logging
logWarning "Empty input"
processLinesLog
n -> do
logDebug "Correct line"
logInfo $ "Line length: " <> Text.pack (show n)
```
Let's summarize required changes:
1. Make type more polymorphic: `(WithLog env Message m, MonadIO m) => m ()`
2. Add `liftIO` to all `IO` functions.
3. Replace `putStrLn` with proper `log*` function.
## Running actions
Let's run both functions:
```haskell
main :: IO ()
main = do
processLinesBasic
let action = cmap fmtMessage logTextStdout
usingLoggerT action processLinesLog
```
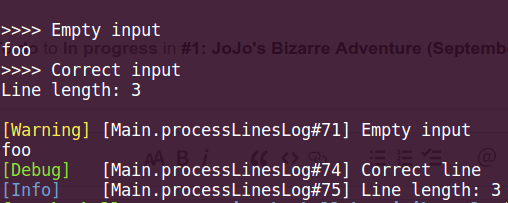
And here is how output looks like: